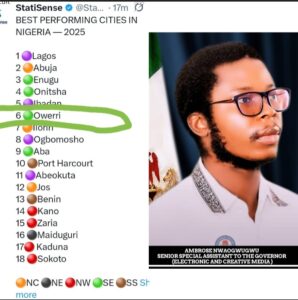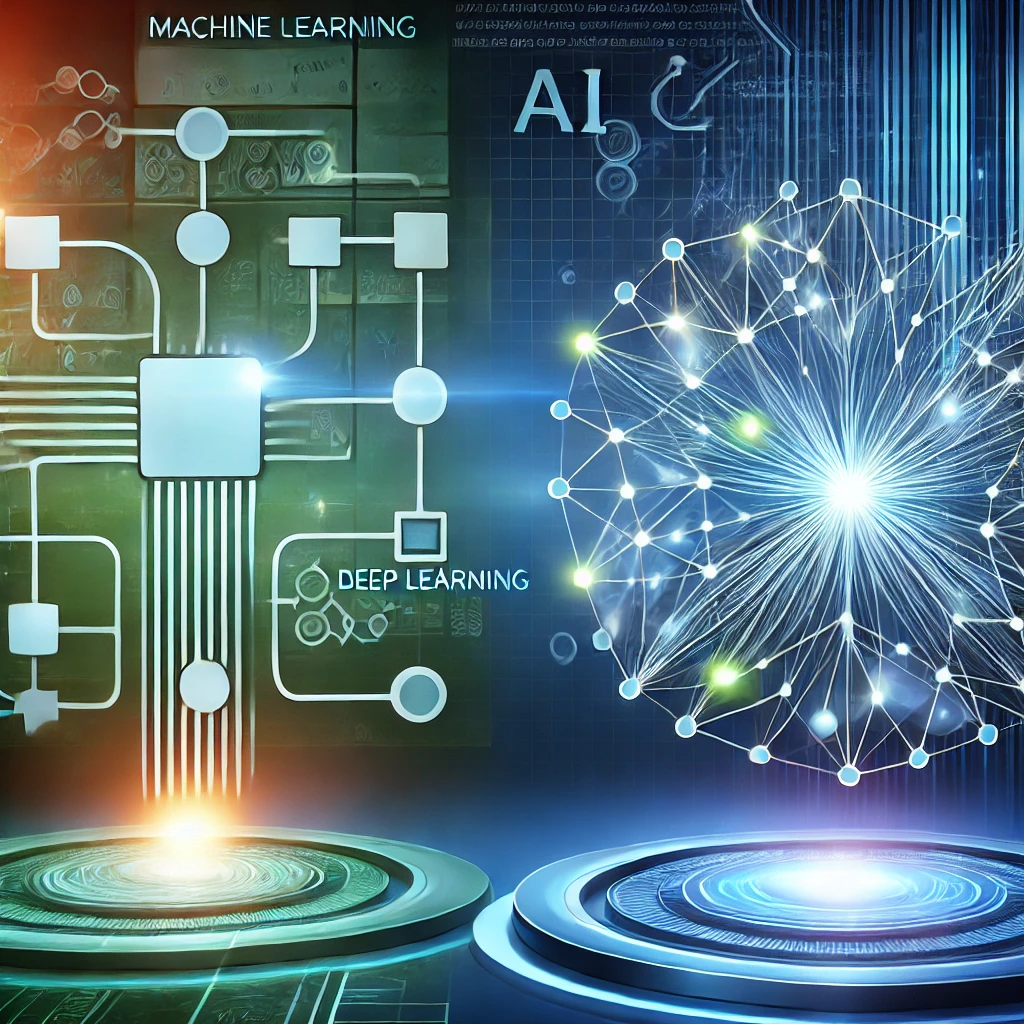
A comparative illustration showing machine learning with a simple neural network and deep learning with a complex layered neural network
Understanding Deep Learning vs. Machine Learning

Understanding Deep Learning vs. Machine Learning.
In the age of artificial intelligence (AI), the terms deep learning and machine learning are often used interchangeably. However, they are distinct subsets of AI, each with unique applications and methodologies. This article delves into the key differences between deep learning and machine learning, helping you understand their roles, advantages, and limitations.
—
What Is Machine Learning?
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of AI that allows systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed. It relies on algorithms to identify patterns, make decisions, and predict outcomes.
How Machine Learning Works
Machine learning models are typically trained using structured data. The process involves:
1. Data Input: Collecting and preprocessing data.
2. Training the Model: Feeding the data into an algorithm to establish relationships.
READ ALSO: Top 5 Ways to Monetize Your Blog in 2024.
3. Validation and Testing: Ensuring the model performs accurately on new data.
Applications of Machine Learning
Fraud detection in banking.
Email spam filtering.
Recommendation systems (e.g., Netflix, Amazon).
Predictive maintenance in industries.
—
What Is Deep Learning?
Deep learning (DL) is a specialized branch of machine learning. It uses neural networks that mimic the human brain to process vast amounts of unstructured data.
How Deep Learning Works
Deep learning involves deep neural networks with multiple layers. Each layer processes input data, extracting increasingly complex features to generate predictions or classifications.
Applications of Deep Learning
Image and speech recognition.
Autonomous vehicles.
Natural language processing (NLP) for chatbots.
Medical imaging for disease detection.
—
Key Differences Between Deep Learning and Machine Learning
—
Advantages and Disadvantages
Machine Learning
Advantages:
Easier to implement and train.
Less computationally intensive.
Suitable for smaller datasets.
Disadvantages:
Limited accuracy for complex problems.
Requires manual feature engineering.
Deep Learning
Advantages:
Handles unstructured data (images, videos, text).
High accuracy for complex tasks.
Continuous learning as more data becomes available.
Disadvantages:
Computationally expensive.
Requires vast amounts of data.
Harder to interpret model decisions.
—
Choosing Between Deep Learning and Machine Learning
The choice between ML and DL depends on the project requirements:
Opt for machine learning when working with structured data and limited computational resources.
Use deep learning for tasks involving unstructured data and large datasets, where precision is paramount.
—
Future Trends in AI
As technology advances, the gap between ML and DL is narrowing. Emerging trends include:
Hybrid Models: Combining ML and DL for enhanced efficiency.
Explainable AI: Making deep learning models more transparent.
Edge AI: Running AI models locally on devices, reducing dependency on cloud computing.
—
Conclusion
Both machine learning and deep learning are powerful tools in the AI arsenal. While machine learning is ideal for simpler, structured tasks, deep learning thrives in complex, unstructured environments. Understanding their strengths and limitations will help you choose the right approach for your needs.